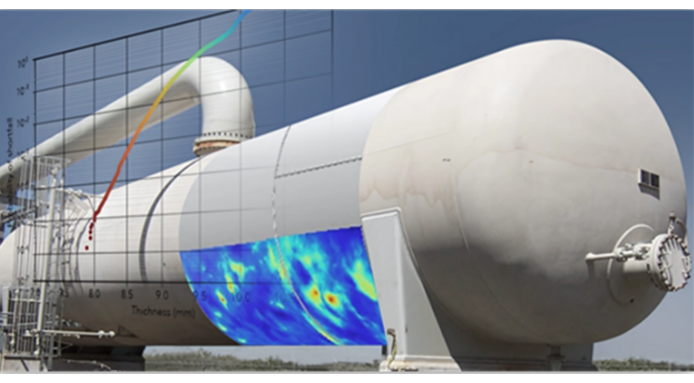
For inspection and integrity engineers, responsible for the integrity of pressure vessels, understanding the pros and cons of different inspection methodologies is vital. While Internal Visual Inspection (IVI) has been used traditionally by the industry as a preferred way of inspecting the internal condition of pressure vessels, Non-Intrusive Inspection (NII), guided by the HOIS-RP-103 Recommended Practice, offers a structured and often more efficient alternative.
The Foundation of Non-Destructive Testing
As a baseline understanding, Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) provides the essential toolkit. These are the diverse techniques – from ultrasonic testing to advanced radiography – that allow us to probe materials and components for flaws without breaking the pressure envelope. NDT is the bedrock of modern integrity assessment. However, applying NDT techniques ad-hoc will not lead to demonstrable confident in the true state of the vessel.
HOIS-RP-103 Defined Process (NII Framework)
For pressure vessels, NII is more than just a set of NDT techniques. It’s a rigorous, 4-stage process meticulously outlined in HOIS-RP-103, the industry-leading Recommended Practice. This framework, developed under the HOIS Joint Industry Project (JIP), and co-authored by ESR Technology, provides the definitive guide and framework for non-intrusive pressure vessel inspection.
NII provides a structured methodology that is responsive to the corrosion threat, optimising coverage and defining required NDT technique performance to ensure a rigorous, statistical assessment of the current internal state. Implementation provides an auditable and reliable inspection regime.
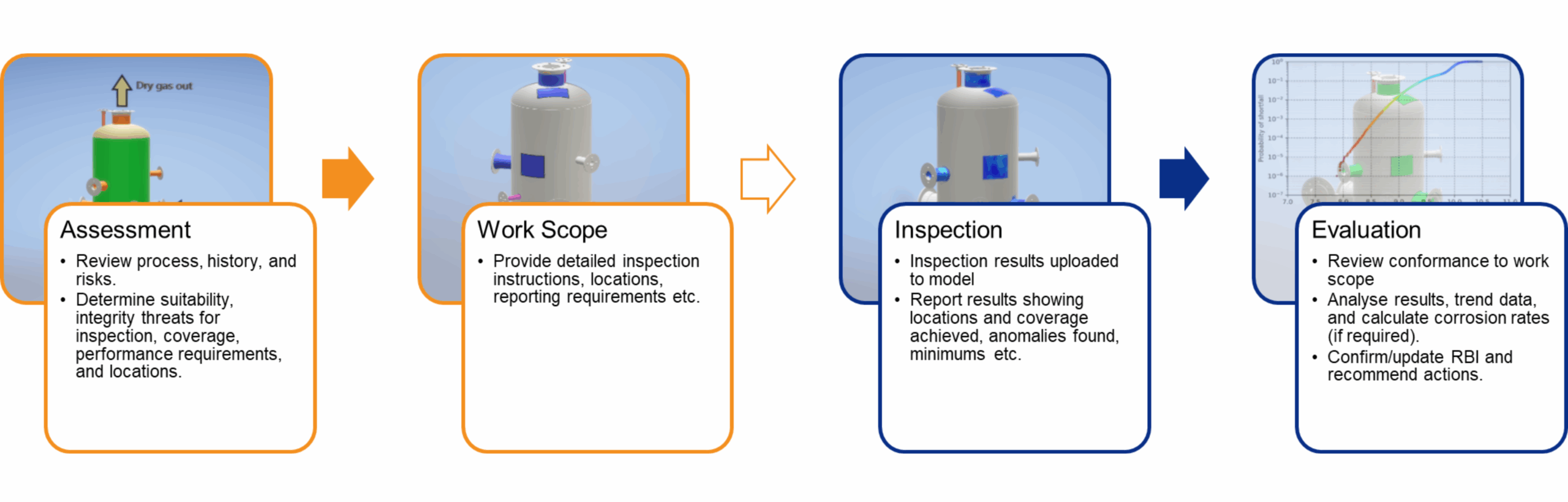
The 4 Stages of the NII Process
The HOIS-RP-103 framework is built upon a clear and logical 4-stage process, ensuring thoroughness and informed decision-making:
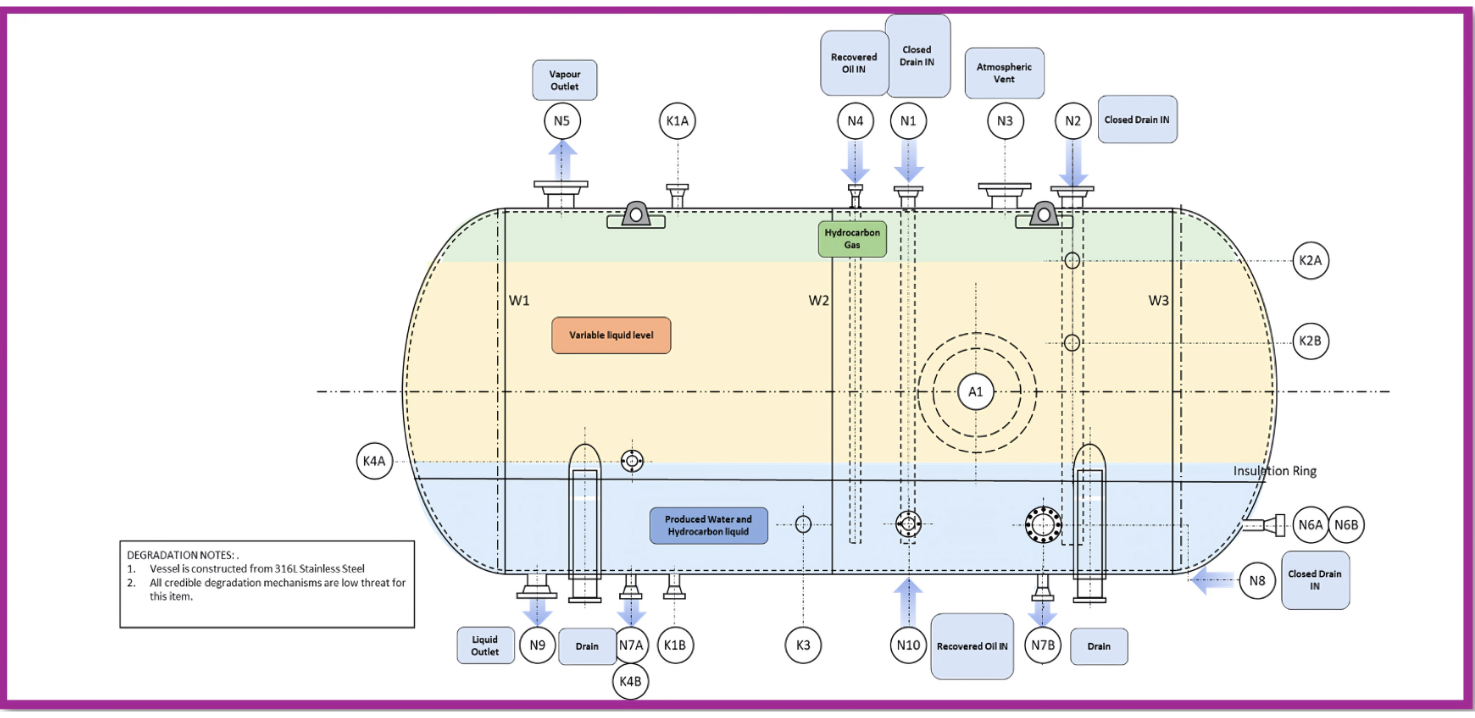
- NII Assessment: Is NII Right for Your Vessel? This initial stage is crucial for determining NII applicability. Integrity and Inspection Engineers conduct a comprehensive evaluation of vessel design, operating history, process conditions, and a mandatory corrosion risk assessment. This rigorous assessment, as per the recommended practice, dictates whether NII is a suitable way forward for inspection, inspection performance requirements and the coverage.
- NII Workscope: When NII is deemed appropriate according to the framework, a precisely defined work scope is developed. This involves defining inspection locations based on the spatial nature of corrosion and specifying the NDT techniques (from ultrasonics to radiography and beyond) to be employed at each location. This targeted statistical approach optimises the inspection whilst providing confidence in the integrity state.
- Inspection Execution: In this stage, qualified personnel expertly apply the NDT techniques defined in the NII Work Scope and in strict adherence to the recommended practice. Inspections are conducted externally, gathering critical data without the need for hazardous internal vessel entry. NDT techniques such as phased array ultrasonic testing or Time-of-Flight Diffraction (TOFD) are some examples of methods employed within the NII process, always within this structured framework.
- NII Evaluation: The final and vital stage is the rigorous statistical evaluation of the inspection data. Experienced consultants at ESR Technology assess whether the inspection met the aims of the work scope, determine whether there are signs of early onset corrosion, estimate the overall minimum wall thickness and corrosion rate. A key outcome, as dictated by the recommended practice, is a clear determination of whether the NII results can confidently replace a traditional IVI, meeting the principles of NII defined within the HOIS-RP-103 document.
The Tangible Advantages of Compliant NII
Implementing NII within the HOIS-RP-103 framework delivers clear and measurable benefits:
- Enhanced Safety: Process-Driven Risk Reduction. The systematic approach prioritises safety by design. By minimising or eliminating confined space entry, NII significantly reduces risks to inspection personnel, a core benefit which drives the methodology.
- Production Uptime: The wholly externally applied NDT inspection translates to minimised downtime. There is no requirement to limit inspection to shut-downs and NII inspections can be carried out year-round. NII inspections can also be carried out at elevated temperatures reducing the requirement to cease production for inspection.
- Cost Efficiency: Although NII inspections can have more direct inspection costs. With no requirement to clean the interior of the vessel or construct internal scaffolding and no loss of production NII can result in overall savings in operation expenditure.
Key NII Distinctions
- NII, in accordance with HOIS-RP-103, is not just externally applied inspection: it’s the defined auditable process. It is a specific, 4-stage methodology defined by industry best practice, not a generic term.
- NII, in accordance with HOIS-RP-103, is a rigorous statistical approach. The inspection is part of a feedback loop and is responsive to the corrosion threat assessment for individual vessels..
Moving Beyond
In conclusion, while NDT provides the essential tools for non-destructive testing evaluation, NII guided by the HOIS-RP-103 Recommended Practice and managed by ESR Technology, offers a superior, structured process for pressure vessel integrity management. Understanding this critical distinction is vital for engineers seeking to ensure safety and cost-effectiveness of their equipment inspection strategies. Adopting frameworks like this is not just best practice; it’s the pathway to unlocking safer, smarter, and more reliable inspections for the future.
Contact ESR Technology to discuss your NII implementation and training requirements.
Find this article useful? Gain more insight on NII process implementation benefits – Download HOIS G 103 guidance documents here
To purchase HOIS RP 103, click here.